Gastrointestinal Upset?
Nutritional Deficiencies?
Consider the Pancreas
Exocrine Pancreatic Insufficiency (EPI)—Decreased Production, Delivery, or Activity of Pancreatic Enzymes Needed for Proper Digestion
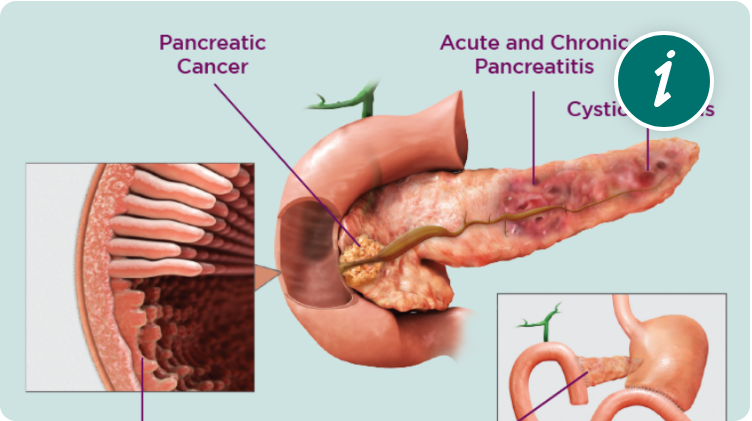
EPI Is Caused by Various Pancreatic and Extrapancreatic Conditions1,2*
EPI Signs and Symptoms1,2
- Flatulence
- Bloating
- Abdominal discomfort
- Fatty food intolerance
- Diarrhea
- Malodorous stool
- Steatorrhea
EPI Can Have Nutritional Consequences and Impact Quality of Life1,2
- Micronutrient and fat-soluble vitamin deficiencies
- Malnutrition
- Weight loss
OBSERVED IN PATIENTS WITH CHRONIC PANCREATITIS
- Impaired quality of life3
- Increased mortality4
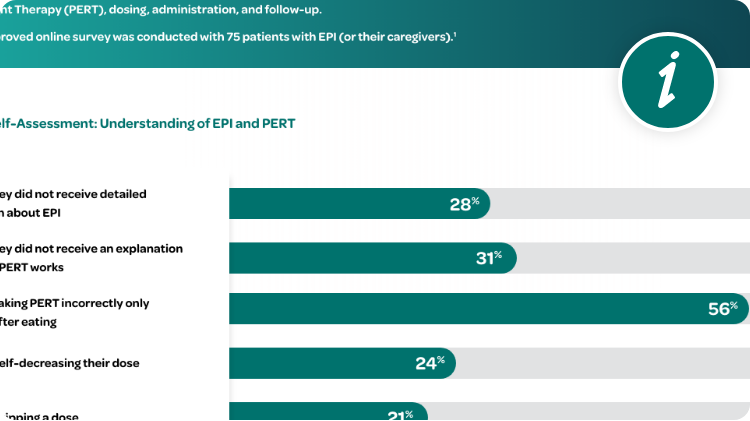
EPI Is Largely a Clinical Diagnosis
Considerations in the diagnosis of EPI
PRESENCE OF EPI-PREDISPOSING CONDITION5,6
- Cystic fibrosis
- Chronic pancreatitis
- Acute pancreatitis
- Pancreatic/gastric surgery
- Pancreatic cancer
- Inflammatory bowel disease
- Celiac disease
SIGNS & SYMPTOMS5,6
- Flatulence
- Bloating
- Abdominal discomfort
- Fatty food intolerance
- Diarrhea
- Malodorous stool
- Steatorrhea
- Micronutrient deficiencies
- Fat soluble vitamin deficiencies
- Malnutrition
- Weight loss
SUPPLEMENTAL TESTS5,6
- Fecal elastase-1 test
- Fecal fat tests
- Biochemical markers of nutritional status
- Direct pancreatic function test
PATIENT FACTORS THAT MAY DELAY DIAGNOSIS7,8
- Accustomed to symptoms
- Restricting fat intake to avoid symptoms
- Embarrassment
PERT Is the Cornerstone of EPI Treatment
Pancreatic enzyme replacement therapy (PERT)-a combination of porcine-derived lipases, proteases, and amylases to aid digestion5,9
- Dosing options are based on
Patient
weight
Fat content
of the diet
Underlying
condition*
- Dose should be individualized based on
Clinical
symptoms
Fat content
of the diet
Degree of
steatorrhea