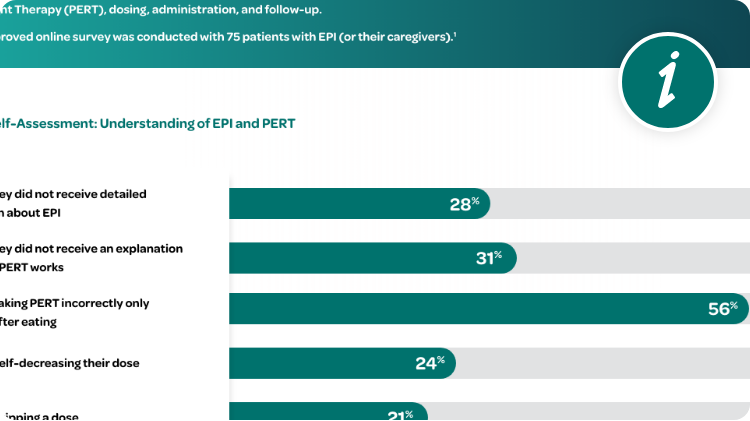
EPI in Primary Care
Introduction
Exocrine pancreatic insufficiency (EPI) is a condition that occurs due to a reduction in pancreatic enzyme production, delivery, and/or activity to a level below the threshold required to maintain normal digestion. EPI results in impaired digestion and decreased absorption of nutrients.1,2
1
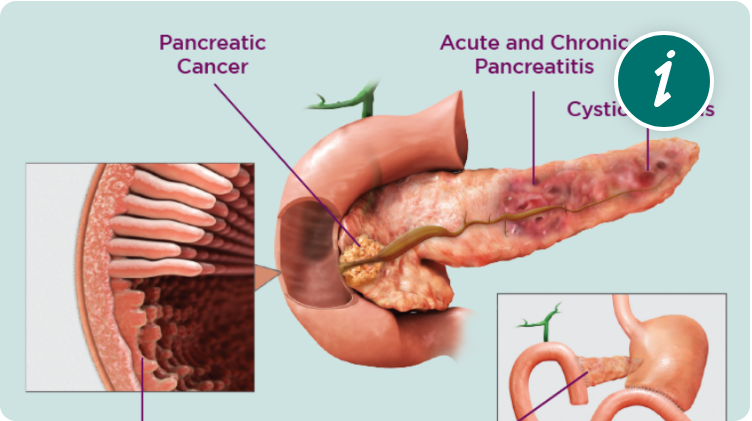
EPI should always be considered in individuals with a newly diagnosed pancreatic disease predisposing to EPI, including chronic pancreatitis, cystic fibrosis, pancreatic cancer, pancreatectomy, and gastrointestinal surgeries.3*
2
Investigate EPI if suggestive signs and symptoms develop in a patient with a known pancreatic disease or in patients with a predisposing condition.
The following signs and symptoms should be considered suggestive of EPI:
3
For patients with a condition predisposing to EPI, regular screening should include:
4
For patients with signs or symptoms suggestive of EPI, thorough investigation should include the following considerations: